What Types Of Graphics Card Slots Are Out There?
Over the years, computers supported different slots for dedicated graphics cards to your computers. Some of them were made for graphics cards along. In this post, we will look at the various types of these slots. Which appeared on motherboards over the year, and how each kind was more advanced than the one before. We will also take a look at integrated graphics, which’s a type of graphics cards to get if you don’t need too much graphical power.
While most of these slots are not in use today, you can find many motherboards & cards that supported them used from eBay. For that purpose, I have added links to that below each type, so you could check their availability or price.
Now, let’s get started~
Quickly go to:-
Integrated Graphics

As its name implies. Integrated graphics card is integrated into the motherboard chipset, or inside the CPU itself. Unlike all the other graphics card types mentioned here. Integrated graphics don’t have its own memory, it uses the main ram instead. This can greatly affect their performance, but for that very reason, they tend to be cheap.
Integrated graphics are common in business laptops. Since one wouldn’t need too much graphical power if you plan on using the computer for typing reports, spreadsheets editing or sending E-Mails. They are also good and more than capable for running older games. They may also allow you to play a limited set of modern games on low settings, but I advise you to not push your luck with one if you really care about that.
Many motherboards come with integrated graphics off the bat, with the ability to add a dedicated graphics card whenever you need to. In case of laptops, you need to weight your options, as it’s usually won’t be possible to change your graphics card.
Another name for Integrated Graphics is On-Board graphics. Intel HD graphics is one of the known ones.
ISA (1981 – 1993~)

ISA stands for Industry Standard Architecture. It is the oldest & slowest slot we discuss here. It supported a bandwidth of up to 8 MB/S. Came in 8-bit & 16-bits versions. There was an attempt to produce a 32-bits version, but it failed.
Because it was a generic expansion slot, ISA supported other types of devices besides graphics cards, like modems, sound cards and more. One of the most common peripherals used on it was the Ad Lib sound card.
PCI completely replaced ISA later on, not just for graphics cards, but for all sort of devices.
Buy and check the price of ISA Graphics Cards on eBay:-

PCI (1992-2004~)
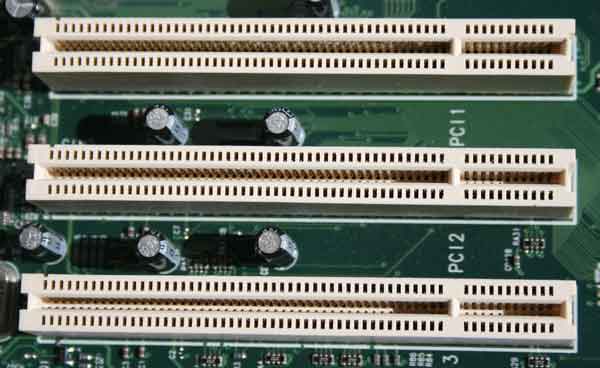
Created in 1992. PCI stands for “Peripheral Component Interconnect”. Before it was replaced by AGP many years later, it used to be the standard slot to add a graphics card after ISA, until the increasing needs for bandwidth outgrew the bandwidth it provides. It had multiple versions, starting from V 1.0, which appeared in 1992, to V 3.5, which appeared in 2004. It supported multiple bus bandwidths:-
-
- 32-bit version, supported bandwidth of 133 MB/s at 33 MHz – this is the standard configuration
- 32-bit version, supported bandwidth of 266 MB/s at 66 MHz or 64-bit at 33 MHz
- 64-bit version, supported bandwidth of 533 MB/s at 66 MHz
PCI is also known as conventional PCI, Parallel PCI or Legacy PCI. These names help us distinguish it from the modern PCI Express slot, which we will talk about in more details later in this article. As for the time of me writing this post, there’s not many motherboards that support it, and it’s a matter of time when you won’t find any.
Besides graphics cards, PCI supported all sorts of devices, not just graphics cards, from sound cards, USB ports cards, network cards, modems and more. Many of these functionalities are done using PCI-E nowadays, making the slot only viable to those with legacy hardware that still works (and so their owners have no reason to replace them).
Buy and check the price of PCI Graphics Card on eBay:-

AGP (1997~ – 2004)

Originally appeared in 1997. AGP stands for “Accelerated Graphics Port”. Unlike PCI, which was designed to attach all sorts of hardware to a computer, including graphics & sound cards. AGP was designed specifically for graphics cards, and its design was based on the PCI slot.
AGP allows the graphics card to communicate directly to the CPU. It doesn’t share the bus of any PCI slot on the same motherboard. It supported higher transfer rates than legacy PCI slots, and used a simpler handshaking process. Just like the case of PCI-E, AGP supports multiple speeds:- 1X, 2X, 4X or 8X. It also came in multiple versions, starting from AGP 1.0, and up until AGP 3.5. You can see the technical details in the following table:-
| Specification | Voltage | Clock | Speed | Transfers/clock | Rate (MB/s) |
| AGP 1.0 | 3.3 V | 66 MHz | 1× | 1 | 266 |
| AGP 1.0 | 3.3 V | 66 MHz | 2× | 2 | 533 |
| AGP 2.0 | 1.5 V | 66 MHz | 4× | 4 | 1066 |
| AGP 3.0 | 0.8 V | 66 MHz | 8× | 8 | 2133 |
| AGP 3.5* | 0.8 V | 66 MHz | 8× | 8 | 2133 |
AGP was started to be replaced by PCI-Express starting from 2004. By 2008, it was harder to find AGP cards in the market.
Buy and check the price of AGP Graphics Card on eBay:-

PCI-Express
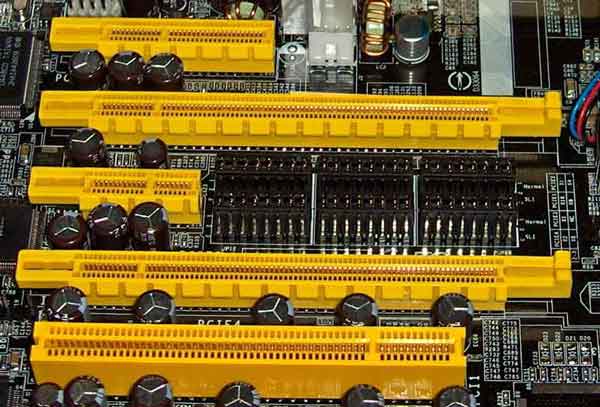

PCI-Express is the most widely used expansion slot nowadays. If you bought a brand-new graphics card today, it’s going to require PCI-Express slot on your motherboard. PCI-Express is also known as PCI-E, it supports multiple speeds:- 1X, 2X, 4X, 8X, & 16X (The length of the slot determines the speed, see the various slots in the picture for reference). Both your motherboard & card has to support the speed in order to benefit from it. It provides the most bandwidth among all the graphics cards slots we talk about here (up 63.02 GB/s, according to PCI-E V 5.0, the next version allows for double that). You can see technical details on all PCI-E versions in the following table, including the bandwidth:-
| PCI Express | Introduced | Line | Transfer | Throughput | ||||
| version | code | rate | x1 | x2 | x4 | x8 | x16 | |
| 1 | 2003 | 8b/10b | 2.5 GT/s | 250 MB/s | 0.500 GB/s | 1.00 GB/s | 2.0 GB/s | 4.0 GB/s |
| 2 | 2007 | 8b/10b | 5.0 GT/s | 500 MB/s | 1.000 GB/s | 2.00 GB/s | 4.0 GB/s | 8.0 GB/s |
| 3 | 2010 | 128b/130b | 8.0 GT/s | 984.6 MB/s | 1.969 GB/s | 3.94 GB/s | 7.88 GB/s | 15.75 GB/s |
| 4 | 2017 | 128b/130b | 16.0 GT/s | 1969 MB/s | 3.938 GB/s | 7.88 GB/s | 15.75 GB/s | 31.51 GB/s |
| 5 | 2019 | 128b/130b | 32.0 GT/s[iv] | 3938 MB/s | 7.877 GB/s | 15.75 GB/s | 31.51 GB/s | 63.02 GB/s |
| 6.0 (planned) | 2021 | 128b130b & PAM-4 | 64.0 GT/s | 7877 MB/s | 15.754 GB/s | 31.51 GB/s | 63.02 GB/s | 126.03 GB/s |
Nowadays, it’s common for motherboard contains more than one PCI-E slot. If your motherboard contains multiple PCI-E ports, make sure you install your graphics card in the fastest ones. It’s uncommon for the different slots on the same motherboard to have different speeds. e.g. One slot supports 16X, while the other two support 8X only. For that reason, it’s better to consult your motherboard manual to know the details.
Buy and check the price of various PCI Express graphics cards in Amazon & eBay:-
#CommissionsEarned





Conclusion
We have gone through multiple graphics cards slot types that were used in the last decades. And there’s no doubt that PCI-E could be replaced by an even better someday in the future. That may not happen soon, as we keep getting new versions of it, just like we did for AGP back in the day. For the most part, those looking to buy a new computer only need to know whether they should get a dedicated or integrated graphics. If you’re into buying an old PCs to play older games on, in which case knowing about the older slots types can help you a lot there.
I hope this post helped you know the difference between the different graphics card slots. I hope to see you again in another article.
Sources & Useful Links
- Industry Standard Architecture (Wikipedia)
- PCI Express (Wikipedia)
- Accelerated Graphics Port (Wikipedia)
- Conventional PCI (Wikipedia)


I had no idea EISA failed. It was definitely niche and replaced by PCI/AGP as much better alternatives but I don’t think I would call it a failure as computers supported it and their were AICs on the market which benefited from it. I would classify it with MFM drive technology.
They might have been referring to VESA Local Bus, it was certainly short lived. I had both VLB and EISA and from what I recall they worked about the same.
Some clarity is needed.
1. ISA always is 16 Bit. Never 8 Bit. 8 Bit is the shorter IBM PC slot introduced in 1981. It is the oldest “PC” slot (APPLE II, S-100, ZX-81,and others are older still). The term “ISA” was defined by the “Gang of 9” to avoid conflict with IBM’s original 1984 AT slot which is the same. ISA is the 2nd oldest “PC” slot. An 8 bit PC slot card will fit and work in an ISA slot.
2. The IBM PC 8 bit slot was the FIRST “PC” video slot. MGA, CGA, and EGA cards are 8 Bit PC slot video cards.
3. EISA is the same size as the ISA slot but it has a second set of deeper pins to make it 32bit. It was introduced in 1988 5 years before PCI (1993). While there were EISA video cards, it’s claim to fame was 32bit SCSI hard drive controller cards for workstations/servers. Not a failure by any means. You can put an ISA card into an EISA slot and it will work. As will an 8 bit PC card. 3 for the price of one. Not a waste on the motherboard.
4. In 1987 IBM introduce the MCA slot for it’s PS/2 computers. Initial IBM PS/2 computers had VGA built into the motherboard, later on IBM released the MCA VGA cards. Third parties released VGA ISA cards prior to PCI to avoid IBM MCA slot royalties.
5. VLB ( VESA Local Bus). Introduced in 1992 to speed up the ISA/EISA video bottleneck, it was tied to the 486 chip architecture and so is found mostly (if not all) on 486 motherboards. PCI came a year later and was significantly faster and (drumroll…) worked with the new Pentium chips. Primarily for video but were also made in combo cards that had serial, game, printer, hard drive/floppy drive controllers etc. PCI killed VLB.